
In animal cells, two pairs of centrioles formed from the replication of one pair are located outside of the nucleus.Īt the end of interphase, the cell enters the next phase of meiosis: Prophase I. During prophase, the nucleolus disappears, the nuclear envelope starts to fragment, and the DNA and associated.The nucleus is bounded by a nuclear envelope and the cell's chromosomes have duplicated but are in the form of chromatin.In the latter part of interphase, the cell still has nucleoli present. During prophase and metaphase of mitosis, each chromosome exists in the above state.chromosome condensation Mitosis begins at prophase with the thickening and coiling of the chromosomes. Note that the G in G2 represents gap and the 2 represents second, so the G2 phase is the second gap phase. prophase, the initial stage of mitosis and of the mitotic division of meiosis, characterized by the formation of the mitotic spindle and the condensation of the chromosomes. During prophase (pro-faze), the first stage of mitosis, the chromatin (diffuse strands of genetic material) coils tightly, forming structures that are. The cell synthesizes proteins and continues to increase in size. G2 phase: The period after DNA synthesis has occurred but prior to the start of prophase.In most cells, there is a narrow window of time during which DNA is synthesized.
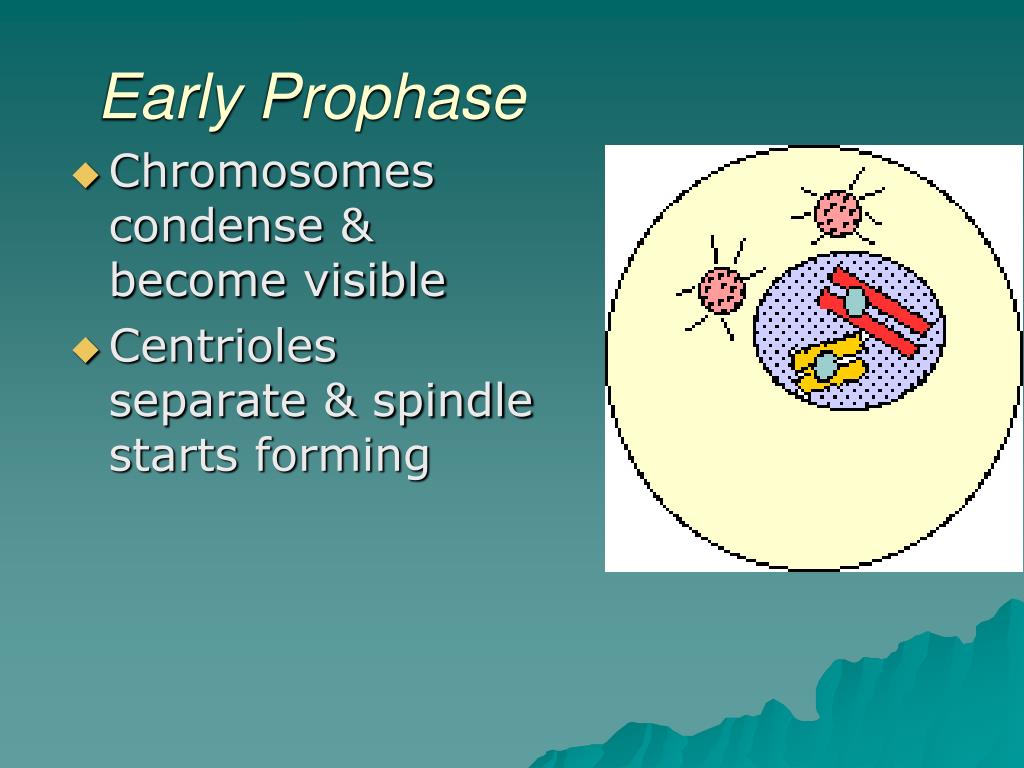
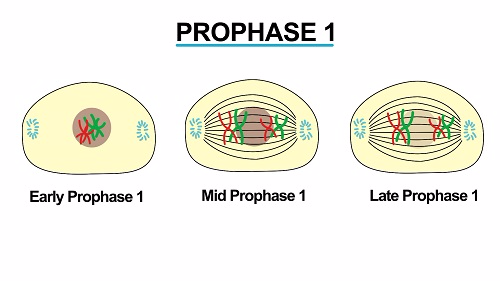
During prophase, the cell becomes spheroid while the cytoplasm becomes more refractile and viscous and pale. There are two stages or phases of meiosis: meiosis I and meiosis II. Prophase is the first stage of mitosis which is characterized by the appearance of thin-thread like condensing chromosomes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
